Selenium Course
- 64k Enrolled Learners
- Weekend/Weekday
- Live Class
If you wish to know the easiest way to locate elements on the webpage, then check out the Selenium Certification Training. The best way to locate elements in selenium is using XPath. In this article on XPath in Selenium, I will give you a brief insight on how to create the right and effective XPath along with its various types.
You may also go through this recording of XPath in Selenium where you can understand the topics in a detailed manner with examples.
This video on Xpath Tutorial talks about Xpath fundamentals and steps involved in writing a Xpath Script.

Find out our Selenium Training in Top Cities/Countries
| India | Other Cities/Countries |
| Bangalore | US |
| Hyderabad | UK |
| Pune | Canada |
| Chennai | Australia |
| Mumbai | Singapore |
| Kolkata | Edinburgh |
Now, let’s understand how to write an XPath for an XML Document.
The XML document has a tree-like structure. Below figure is an example of an XML document where you have different tags and attributes. It starts with a tag called the bookstore, which is also an element or a node.
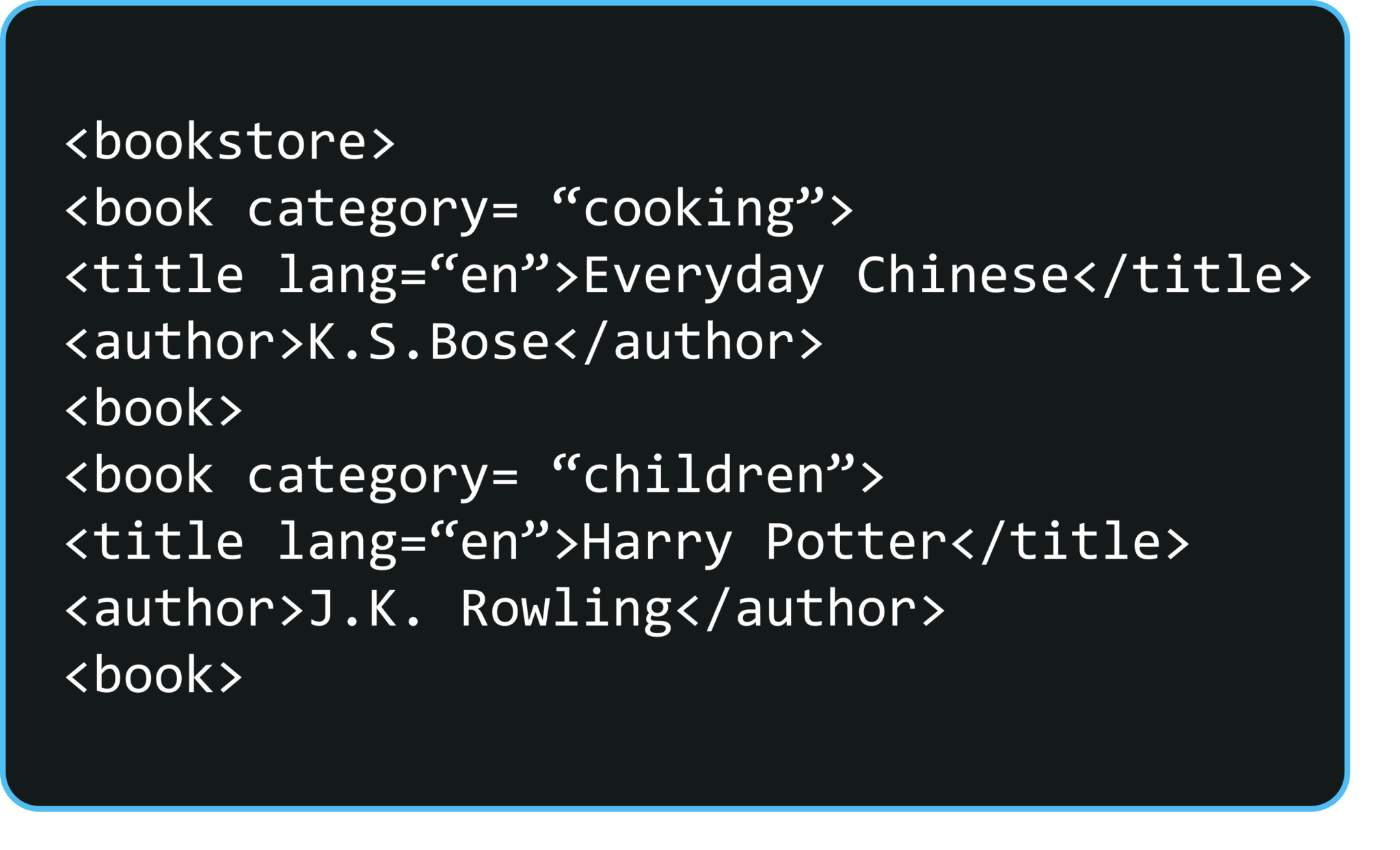 As you can see here, the Bookstore node has a child node Book. It is further followed by an attribute called category whose value is Cooking. And this book node, in turn, has 2 child nodes i.e. Title and Author. Now, let’s visualize this XML document in a tree-like structure. Here, the book store is a root node which has 2 children of type book. Category of 1st book type is cooking and 2nd is children. As you can see in the below figure, both have 2 tags i.e. title and author.
As you can see here, the Bookstore node has a child node Book. It is further followed by an attribute called category whose value is Cooking. And this book node, in turn, has 2 child nodes i.e. Title and Author. Now, let’s visualize this XML document in a tree-like structure. Here, the book store is a root node which has 2 children of type book. Category of 1st book type is cooking and 2nd is children. As you can see in the below figure, both have 2 tags i.e. title and author.
 Here, I will start with the root node i.e. book store, then I will locate a book whose category is children. Once I reach the correct node, the next step will be to pick a node with an author tag. So XPath can be written like:
Here, I will start with the root node i.e. book store, then I will locate a book whose category is children. Once I reach the correct node, the next step will be to pick a node with an author tag. So XPath can be written like:
bookstore/book[@category='children']/author
This is an XPath query to locate the author of a book whose category is children. Now let’s understand the syntax of the XPath query.
Below figure depicts XPath Syntax and its terminology.

In the next section of this XPath in Selenium article, I will be talking about different types of XPath with the help of some practical examples.
There are two types of XPath and they are:
First, let’s understand Absolute XPath.
It is the direct way to find the element, but the disadvantage of the absolute XPath is that, if there are any changes made in the path of the element then that XPath gets failed. For example: /html/body/div[1]/section/div[1]/div
For Relative XPath, the path starts from the middle of the HTML DOM structure. It begins with the double forward slash (//), which means it can search the element anywhere at the webpage. For example: //input[@id=‘ap_email’]
Now, let’s understand this with the help of an example. I will launch Google Chrome and navigate to google.com. Here, I will try to locate the search bar using XPath. On inspecting the web element you can see it has an input tag and attributes like class and id. Now, I will use the tag name and these attributes to construct XPath which in turn will locate the search bar.
 Here, you just have to click Elements tab and press Ctrl + F to open a search box in chromes developers tool. Next, you can write XPath, string selector and it will try to search based on that criteria. As you can see in the above image, it has an input tag.
Here, you just have to click Elements tab and press Ctrl + F to open a search box in chromes developers tool. Next, you can write XPath, string selector and it will try to search based on that criteria. As you can see in the above image, it has an input tag.
Now I will start with // input. Here //input implies tagname. Now, I will use the name attribute and pass ‘q’ in single quotes as its value. This gives XPath expression as below:
//input[@name=’q’]
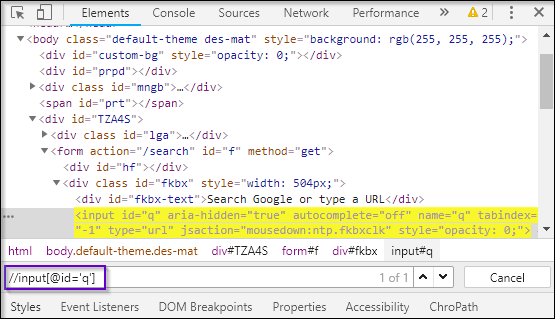 As you can see in the above image, on writing the XPath it has highlighted the element which implies that this particular element was located using XPath.
As you can see in the above image, on writing the XPath it has highlighted the element which implies that this particular element was located using XPath.
Now, let’s move ahead with this XPath in Selenium article and understand different functions used in Selenium.
Automation using Selenium is definitely a great technology that provides many ways to identify an object or element on the web page. But sometimes we do face problems in identifying the objects on a page which have the same attributes. Some of such cases can be: elements having the same attributes and names or having more than one button with the same name and ids. In such cases, it’s challenging to instruct selenium to identify a particular object on a web page and this is where XPath functions come to our rescue.
Selenium is comprised of various functions. Below, I have listed down three of the most widely used functions:
First, I will tell you how contains() function is being used in XPath query.
It is a method used in an XPath expression. When the value of any attribute changes dynamically e.g. login information, this method comes into use. It can locate a web element with the available partial text. Let me show you how to use contains() method.
 I will again open google.com and choose a <img> tag to inspect its element tab. So what’s next?
I will again open google.com and choose a <img> tag to inspect its element tab. So what’s next?
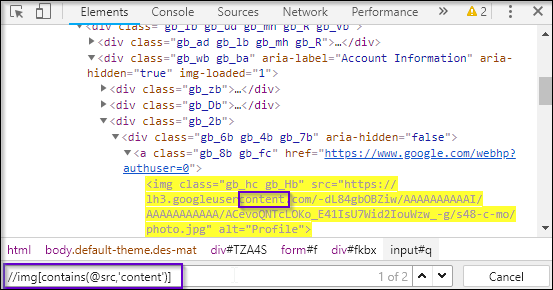
As you can see in the above source code snippet, it has a <img> tag, followed by its attributes. Now let’s say, I want to locate its src attribute using XPath. In order to do this, I will start with // followed by input tag, then I will use the select attribute, followed by its attribute name src. Finally, I will copy and paste the value of src. But by doing this, our XPath will become too lengthy.
And, this is one of the biggest reasons for constructing a partial XPath query. As an src attribute contains the URL in its value, there are chances that its value or some part of the URL might change while you reload the page. So the bottom line here is, a part of the attribute value is static while the rest is dynamic, in such cases, we generally prefer using partial XPath.
XPath query looks like:
//img[contains(@src,’content’)]
Now let’s, move further and understand a few more XPath functions.
This function is used to find a web element whose value of an attribute changes on the refresh or on any other dynamic operation on the web page. In this, we match the starting text of the attribute to locate an element whose attribute has changed dynamically.
For Example: On the web page, ID of a particular element changes dynamically such as ‘id1’, ‘id2’, ‘id3’, etc., but the remaining text will be the same.
Let’s now try demonstrating it using the same object. Here, instead of contains(), you have to change it to starts-with().
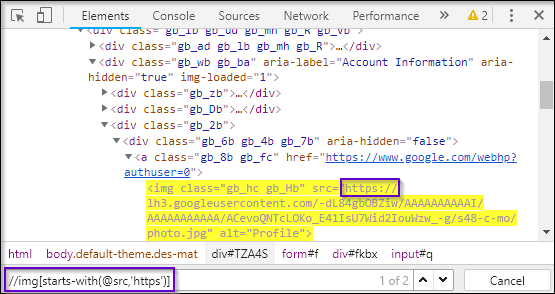 As you can see in the figure src attribute starts with https. It will locate the elements that start with https. Thus, this is how starts-with function is used to locate a particular element on the webpage.
As you can see in the figure src attribute starts with https. It will locate the elements that start with https. Thus, this is how starts-with function is used to locate a particular element on the webpage.
XPath query looks like:
//img[starts-with(@src,'https')]
Now let’s understand one more function text().
This expression is used with the text function to locate an element with exact text. Let’s see a small example to use text().
 Here my condition is –
Here my condition is –
The asterisk(*) implies any tag with the same value. This give me an XPath query that looks like:
//*[text()='Search Google or type a URL']
This is how you can use text() function. Now let’s try to use two functions i.e. contains() and text() together in one XPath query.
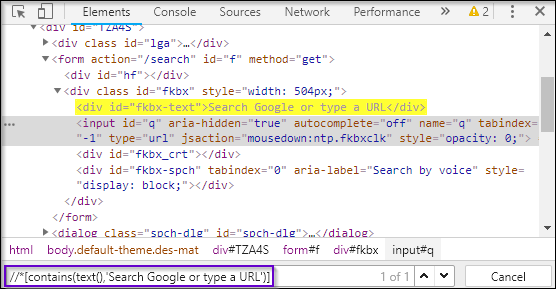 As you can see in the above snippet, first I have used contains(), and passed the first argument as text(). Now, text() should hold a value Search Google or type a URL. As you might notice, I have not used @ because the text() is a function and not an attribute. This is how you can use two XPath functions together.
As you can see in the above snippet, first I have used contains(), and passed the first argument as text(). Now, text() should hold a value Search Google or type a URL. As you might notice, I have not used @ because the text() is a function and not an attribute. This is how you can use two XPath functions together.
In the next section of this article, we will see how to register the drivers for chrome and how to send keys to search element using Eclipse.
For google chrome, you need to install a chrome driver in your system. Now let’s take a closer look at the code. As you can see, I have used System.setproperty() to set the path of chrome driver. Then I am using driver.get() to navigate to ebay.com. Further, using the XPath I am locating search box of the webpage. Now, using sendkeys(), I will be sending the search value as Guitar to redirect to the particular search page.
package Edureka;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import org.openqa.selenium.By;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
public class CustomXpath {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.driver", "C:Selenium-java-edurekachromedriver_win32chromedriver.exe");
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver();
driver.manage().window().maximize();
driver.manage().deleteAllCookies();
driver.manage().timeouts().pageLoadTimeout(40, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.manage().timeouts().implicitlyWait(30, TimeUnit.SECONDS);
driver.get("https://www.ebay.com/");
driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='gh-ac']")).sendKeys("Guitar"); //xpath for search box
WebElement searchIcon = driver.findElement(By.xpath("//input[@id='gh-btn']"));//xpath for search button
searchIcon.click();
}
}
When you run the above Java program, chrome driver will launch Google Chrome and redirect to ebay.com and provide you the preferred search automatically. You can refer below image for the output:

I hope this gives you a clear understanding of how XPath in Selenium works. Thus, it brings us to the end of this article.
Got a question for us? Please mention it in the comments section of XPath in Selenium blog and we will get back to you.
 Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUP
Thank you for registering Join Edureka Meetup community for 100+ Free Webinars each month JOIN MEETUP GROUPedureka.co